Fatty liver disease is a condition that occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. It is a growing concern worldwide, affecting millions of people. This blog will help you in understanding fatty liver, examine their causes, identify the symptoms, and discuss the available treatment options.
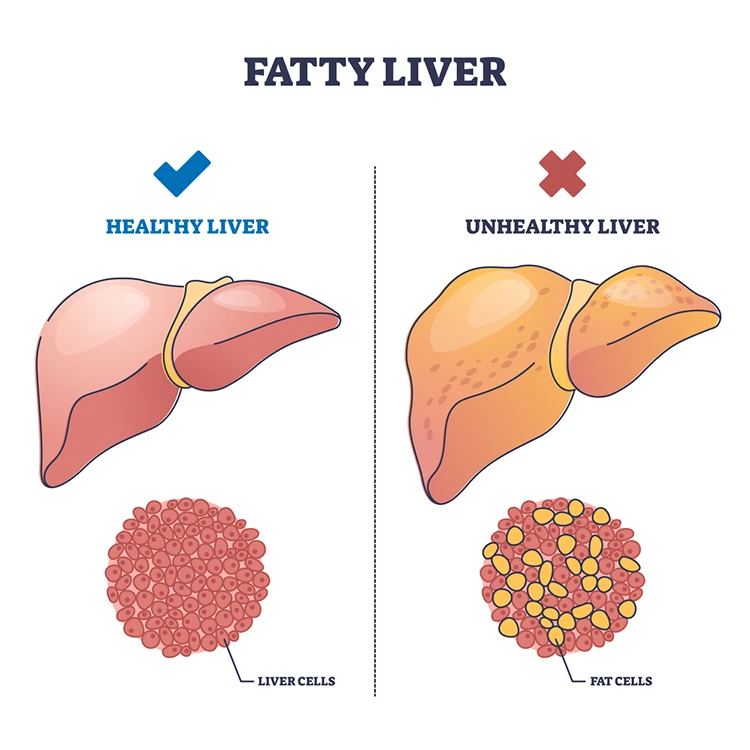
Types of Fatty Liver:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
NAFLD is the most common type of fatty liver and is not caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It is often associated with factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can range from simple fatty liver, where excess fat accumulates in the liver, to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form characterized by inflammation and liver cell damage.
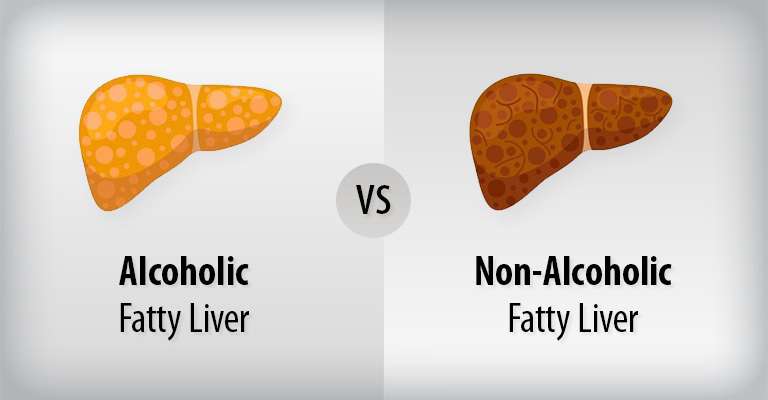
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
AFLD is caused by excessive and chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol is toxic to liver cells, leading to fat buildup and inflammation. AFLD can progress to more advanced liver diseases, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis, if alcohol intake continues.
Causes :
- Poor Diet:
Consuming a diet high in saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars can contribute to the development of fatty liver. These dietary choices promote fat deposition in the liver and increase the risk of liver inflammation. - Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a common risk factor for fatty liver disease. Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, increases the strain on the liver and leads to fat accumulation.
- Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome:
Insulin resistance, often associated with conditions like type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, is a major contributor to fatty liver. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it produces more insulin, which can result in fat accumulation in the liver. - Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption is a leading cause of alcoholic fatty liver disease. Alcohol hampers the liver’s ability to break down fats, leading to fat accumulation and liver damage.(Understanding Fatty liver)
Symptoms of Fatty Liver:
Fatty liver disease may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may manifest:
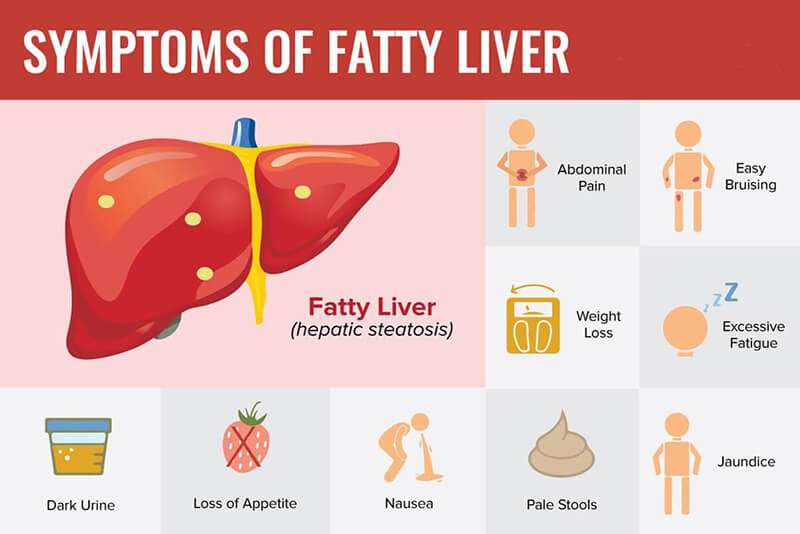
- Fatigue and Weakness:
Reduced liver function can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness due to impaired metabolism and detoxification processes. - Abdominal Discomfort:
Some individuals may experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen due to liver enlargement or inflammation. - Jaundice:
In advanced cases, a yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) may occur, indicating liver dysfunction and impaired bilirubin processing. - Elevated Liver Enzymes:
Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Elevated levels indicate liver inflammation or damage.
Advertisement
Treatment Options for Fatty Liver:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial in managing fatty liver disease. This includes following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Regular exercise and weight loss, if necessary, can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver fat. - Alcohol Moderation or Abstinence:
For individuals with alcoholic fatty liver disease, it is essential to moderate alcohol consumption or abstain from it completely. This allows the liver to heal and prevents further damage. - Medications:
Currently, there are no specific medications approved for treating fatty liver disease. However, healthcare professionals may prescribe medications to manage underlying conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or obesity, which contribute to fatty liver development. - Regular Monitoring:
Individuals diagnosed with fatty liver disease should undergo regular check-ups to monitor liver health. This may involve periodic blood tests, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI, and liver function tests.
Conclusion:
Fatty liver disease poses a significant health risk and affects a substantial number of individuals worldwide. By understanding Fatty liver its different types, identifying the causes and symptoms, and implementing appropriate lifestyle changes, individuals can take control of their liver health. If you suspect you may have fatty liver disease, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember, prioritizing a healthy lifestyle is key to managing and preventing fatty liver disease.
Reference
- Mayo Clinic – Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):**
- [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567](https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567) http://[https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567](https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567)
- Mayo Clinic is renowned for its medical expertise. Linking to their page on NAFLD provides comprehensive information on the condition and dietary recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Try to maintain a healthy weight and eat sensible portions.
Try to lose weight gradually if you’re overweight.
Limit how much fat you eat. …
Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Avoid foods and drinks with large amounts of sugars, especially fructose. …
Avoid heavy alcohol use. …
Quit smoking.
In some cases, the liver damage stops or even reverses itself. But in others, the disease continues to progress. If you have NASH, it’s important to control any conditions that may contribute to fatty liver disease.
Overall, the results derived from these research articles suggest that Liv.52 is beneficial for supportive treatment in improving the symptoms, hepatic parameters, and quality of life in a wide variety of liver diseases like drug-induced hepatotoxicity, hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver.
What foods help fatty liver?
Research suggests it may be beneficial for people with fatty liver disease to incorporate garlic, omega-3 fatty acids, coffee, broccoli, green tea, and nuts into their diet.
Many foods contain specific compounds or antioxidants that have been shown to support liver function. A few examples include grapefruit, blueberries, cranberries, fatty fish, olive oil, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli or Brussels sprouts.

Insightful piece